An eSIM, or embedded SIM, is a digital SIM card embedded directly into a device, eliminating the need for a physical SIM card. Unlike traditional SIM cards requiring manual insertion and replacement, eSIMs are programmable and can store multiple profiles. This innovation has evolved from the limitations of physical SIM cards, offering greater convenience and flexibility for users. In today’s digital world, eSIM technology is increasingly relevant, providing seamless connectivity across multiple devices, enhancing user experience, and supporting the growing demand for global mobility and IoT applications.
What is an eSIM?
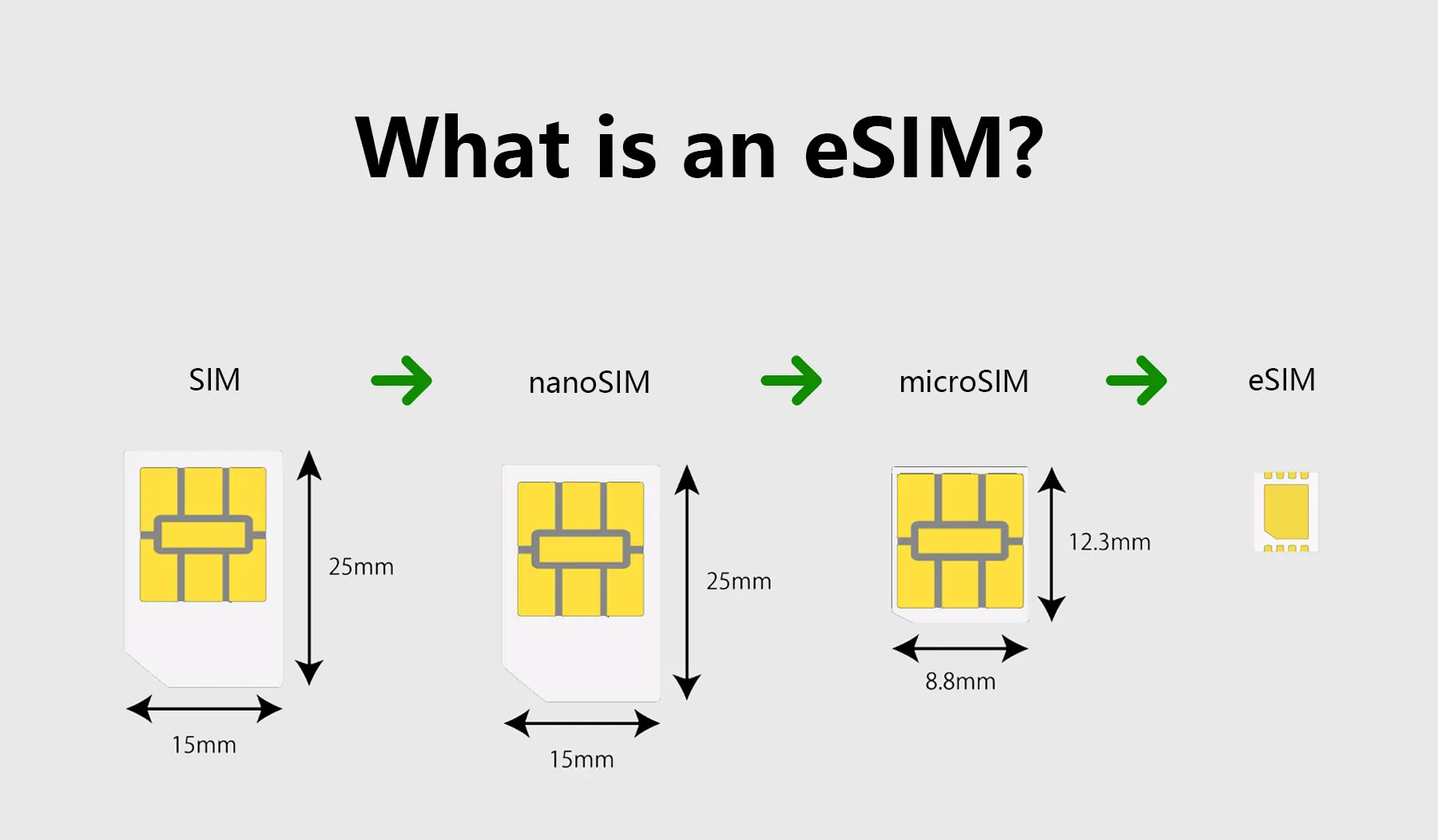
eSIM stands for an “embedded SIM,” a small, programmable chip integrated directly into a device’s hardware. Unlike traditional, removable, physically interchangeable SIM cards, an eSIM is permanently installed within the device. This allows users to switch between carriers and data plans without inserting or removing a physical card.
Technical Overview of an eSIM Technology
eSIM technology is based on a secure element embedded within the device, which stores the user’s profile and network information. This profile can be updated over the air (OTA) using Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP). The eSIM complies with GSMA standards, ensuring interoperability across different devices and networks.
Advantages of an eSIM Technology
- Convenience and Ease of Use: eSIM technology offers unparalleled convenience, allowing users to activate a mobile plan without needing a physical SIM card. Users can switch carriers or plans effortlessly through digital means, such as scanning a QR code or using an app, without visiting a store or receiving a new card.
- Space-Saving in Device Design: Since eSIMs are embedded directly into a device’s hardware, they eliminate the need for a physical SIM card slot. This space-saving feature allows manufacturers to design slimmer, more compact devices or allocate the saved space for other components, enhancing the overall device functionality and design.
- Flexibility in Switching Carriers: eSIMs allow users to switch between multiple carriers or plans without changing their SIM cards. Users can easily compare and choose the best available plans, whether for domestic use or international travel, avoiding roaming charges and staying connected globally.
- Enhanced Security Features: eSIMs offer better security than traditional SIM cards, as they are less prone to physical tampering or theft. The embedded nature of the eSIM makes it harder for unauthorized users to access or swap the SIM, providing an additional layer of protection for the user’s personal data and mobile network access.
- Environmental Benefits: By eliminating the need for physical SIM cards, eSIM technology reduces the production and disposal of plastic and other materials used in SIM cards and their packaging. This reduces electronic waste and promotes a more sustainable, environmentally friendly approach to mobile connectivity.
How an eSIM Works
Process of Activating and Managing eSIM
Activating and managing an eSIM is straightforward and can be done entirely online. Users typically receive a QR code from their carrier, which they can scan with their device to download and activate the eSIM profile. The eSIM profile contains the necessary information to connect to the carrier’s network. This process allows for the easy addition, removal, or switching of carrier profiles without needing a physical SIM card.
Role of QR Codes and Carrier Profiles
QR codes play a crucial role in activating eSIMs. When a user scans the QR code provided by their carrier, it triggers the download of the carrier’s profile to the device. This profile includes all the network settings and authentication details for the device to connect to the carrier’s services. Some carriers also provide downloadable profiles through apps or websites, offering additional methods for eSIM activation. If needed, you can create a QR code using online tools like Adobe Express for demonstration or configuration purposes.
Devices Compatible with an eSIM
List of Popular Smartphones and Devices Supporting eSIM
- Apple iPhone series (starting from iPhone XS and newer)
- Google Pixel phones
- Samsung Galaxy devices (e.g., Galaxy S20 and later)
- Apple iPad Pro models
- Smartwatches like the Apple Watch and Samsung Galaxy Watch
- Laptops and tablets, including Microsoft Surface and Lenovo models
Expansion of eSIM in Various Gadgets
- Wearables and fitness trackers
- IoT devices and smart home products
- Connected car solutions in the automotive industry
- Enhanced interconnectivity in various sectors
Security and Privacy Concerns
eSIM Enhances Security Compared to Traditional SIM Cards
eSIMs offer enhanced security features compared to traditional SIM cards. The risk of SIM card theft or cloning is significantly reduced because they are embedded in the device and cannot be physically removed or swapped. eSIMs support secure remote provisioning and profile management, allowing carriers to update security protocols and settings over the air, further protecting users from potential vulnerabilities.
Potential Risks
Despite the security advantages, eSIM technology has risks. One potential concern is the vulnerability of remote provisioning to cyberattacks, where hackers could attempt to intercept or manipulate the process. To mitigate these risks, users should ensure their devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches, and carriers should employ strong encryption and authentication protocols. Using secure, trusted networks when managing eSIM profiles is essential to avoid exposing sensitive information.
Reliable Carriers and Profiles
Selecting reliable carriers and eSIM profiles is crucial for maintaining security and privacy. Users should choose reputable carriers with a strong track record of protecting customer data and providing secure services. They should verify that the eSIM profiles being activated are from legitimate sources, not potentially malicious entities. Being cautious about where and how eSIM profiles are obtained can help prevent security breaches and protect personal information.
Challenges and Limitations of an eSIM
Limited Carrier Support and Availability
While eSIM technology is gaining popularity, not all carriers globally support it. This limitation can restrict users’ choices and make it challenging for some to find compatible plans or providers, particularly in regions where eSIM adoption is still in its early stages.
Compatibility Issues with Older Devices
Many older devices do not support eSIM technology, limiting its benefits to newer models. Users with older smartphones, tablets, or other gadgets must upgrade to take advantage of eSIM’s features, which can be a significant investment.
Potential Difficulties in Switching Carriers Internationally
Although eSIMs are designed to simplify carrier switching, moving between countries can still be challenging. Not all international carriers support eSIM, and users may encounter issues with network compatibility, pricing, and the availability of local eSIM profiles, which can complicate the transition.
Privacy and Security Concerns
While eSIMs offer enhanced security features, there are still data privacy and security concerns. Since eSIMs rely on remote provisioning and digital profiles, there is a risk of cyberattacks or unauthorized access if the systems are not adequately secured. Users and carriers must ensure robust security measures are in place to protect sensitive information.
Technical Challenges in Implementation and Integration
Integrating eSIM technology into devices and networks presents technical challenges, including ensuring interoperability across different platforms and carriers. Manufacturers and carriers must collaborate closely to ensure seamless user experiences, and the technology’s complexity can sometimes lead to compatibility or performance issues. Transitioning from traditional SIM cards to eSIMs requires significant infrastructure investment and changes, which can be a barrier for some carriers and regions.
Conclusion
eSIM technology offers significant advantages, including enhanced security, convenience, device design, and flexibility of carrier selection. While there are challenges, such as limited carrier support and compatibility issues, the potential of eSIM to revolutionize connectivity is immense. As the technology continues to evolve and expand, it presents an exciting opportunity for users to enjoy a more seamless and secure digital experience. We encourage readers to explore eSIM-compatible devices and experience the benefits of this innovative technology.