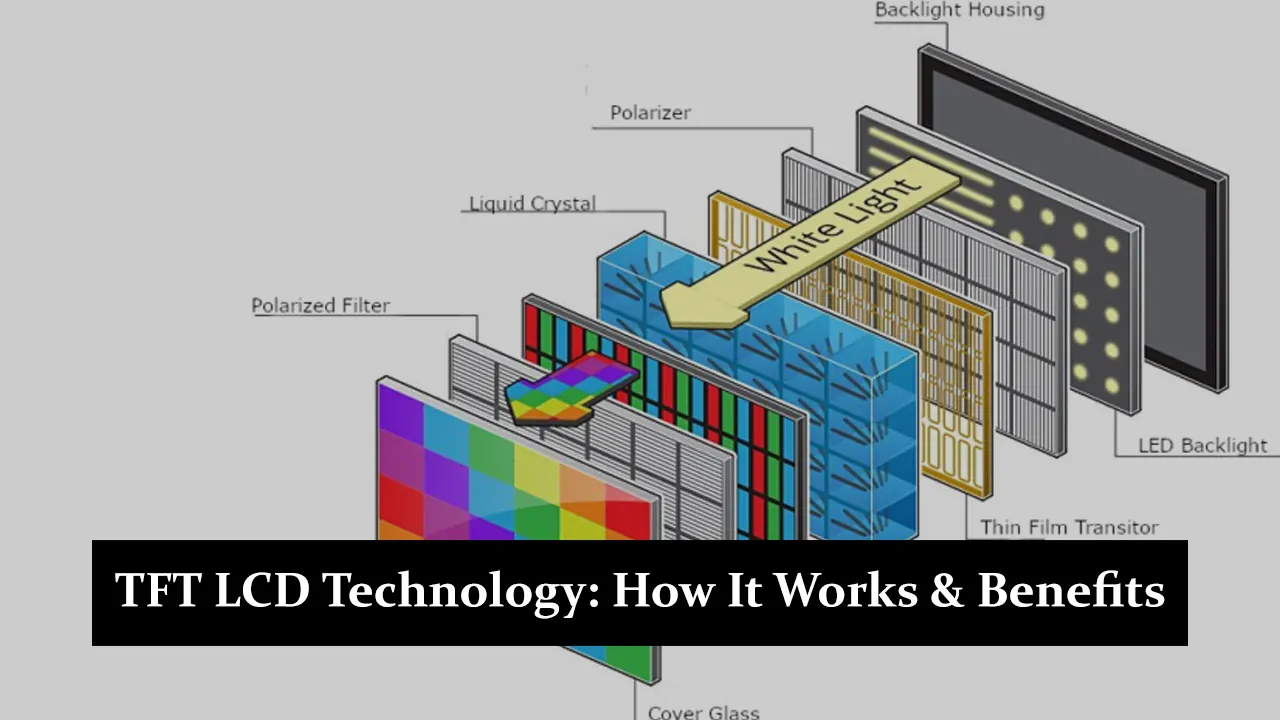
TFT LCD, or Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display, is a popular technology in many modern devices. It controls individual pixels on the screen with thin-film transistors, giving clear and vibrant images. Due to their high-quality visuals and energy efficiency, TFT LCDs are widely used in smartphones, laptops, TVs, and monitors. This technology has become important because it provides sharper images and better colour accuracy than older LCDs. As a result, TFT LCD technology has become a standard in today’s electronics.
What is TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD?
TFT LCD stands for Thin thin-film transistor Liquid Crystal Display, a type of LCD that uses thin-film transistors to improve image quality and response times. The transistors are embedded in each pixel, allowing better control over individual pixels, resulting in sharper images and faster refresh rates. Unlike traditional LCDs, which rely on passive matrices to control pixels, TFT LCDs use an active matrix system, making them more efficient and providing clearer visuals. This technology helps reduce blurriness and offers better colour reproduction, making it a superior option for modern screens.
How TFT LCDs Work
TFT LCDs use thin-film transistors to control each display screen pixel individually. Each pixel comprises three subpixels (red, green, and blue), and the transistors regulate the amount of light passing through these subpixels to create the final image. A backlight shines through the liquid crystals, and the transistors adjust how much light passes through each pixel, producing the desired colours and brightness. Compared to older LCD technologies like passive matrix displays, TFT LCDs offer faster response times and sharper images. This is because TFT LCDs use an active matrix, where a transistor controls each pixel directly, giving them better accuracy and colour consistency.
Types of TFT LCD Displays
TN (Twisted Nematic) Panels
TN panels are known for their fast response times, making them ideal for gaming and fast-paced video content. However, they require more viewing angles and more accurate colour reproduction than other types.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) Panels
IPS panels are favoured for their excellent colour accuracy and wide viewing angles. These displays are commonly found in smartphones, tablets, and high-end monitors, offering a better visual experience for graphic designers and casual users.
VA (Vertical Alignment) Panels
VA panels best contrast the three types, offering deeper blacks and vivid colours. They are great for watching movies or tasks where colour contrast is important, though their response times can be slower than TN panels.
Advantages of TFT LCD Technology
- Enhanced Display Quality: TFT LCDs provide sharp, clear images with better colour accuracy and brightness, improving the viewing experience.
- Lower Power Consumption: Compared to older display technologies, TFT LCDs use less energy, making them more efficient, especially in portable devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Widespread Application: Due to its high-quality visuals and reliability, TFT LCD technology is commonly used in various consumer electronics, from smartphones and televisions to digital cameras and car dashboards.
- Faster Response Times: With thin-film transistors controlling individual pixels, TFT LCDs offer quicker response times, making them suitable for fast-moving video or gaming applications.
- Improved Contrast and Brightness: TFT LCDs’ active matrix design allows for better control over contrast and brightness levels, leading to more vivid and lifelike images.
Applications of TFT LCDs
Smartphones and Tablets
TFT LCDs are widely used in smartphones and tablets because they produce sharp images, vibrant colours, and fast response times. These qualities make them ideal for displaying high-resolution content, gaming, and media consumption.
Monitors and Televisions
TFT LCD technology is commonly found in computer monitors and televisions. Its ability to provide high-definition visuals and accurate colour reproduction makes it a popular choice for everyday and professional graphic work.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, TFT LCDs are used in control panels, medical equipment, and other devices that require reliable, high-quality displays. Their durability and clarity make them perfect for environments where precise visual data is needed.
Automotive Displays
TFT LCDs are increasingly used in automotive applications like dashboards, navigation systems, and rear-view cameras. Their ability to provide clear visuals in various lighting conditions enhances the driving experience and improves safety.
Challenges and Limitations of TFT LCDs
- Colour Shifting: TFT LCDs can suffer from colour distortion when viewed from certain angles, particularly in TN panels, leading to less consistent image quality from different viewpoints.
- Response Times: While TFT LCDs offer decent response times, they can still be slower than OLED displays, leading to motion blur during fast-paced content such as gaming or action movies.
- Power Consumption in Certain Environments: Though generally efficient, TFT LCDs can consume more power in bright environments with higher brightness levels, reducing battery life in portable devices.
- Technological Limitations Compared to OLED: TFT LCDs cannot produce true blacks like OLED displays, as they rely on a backlight that remains on, limiting their contrast and colour depth, especially in dark scenes.
- Limited Flexibility: Unlike OLED, TFT LCDs are less suitable for flexible or curved displays, which restricts their use in certain innovative designs, such as foldable phones or curved screens.
TFT LCD vs Other Display Technologies
TFT LCD vs OLED
TFT LCDs use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which limits their ability to produce deep blacks and true contrast, unlike OLED displays, where each pixel emits its light. OLEDs offer better power efficiency and faster response times, but TFT LCDs are generally more affordable and still provide good image quality.
TFT LCD vs LED
While both TFT LCD and LED displays use LCD panels, the key difference lies in the backlighting. LED displays use backlighting, which is more energy-efficient and offers better brightness control than traditional TFT LCDs that use CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) backlighting. TFT LCDs are, however, more commonly found in consumer electronics.
TFT LCD vs AMOLED
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays have an active matrix structure similar to TFT LCDs but use organic compounds to produce light. This allows AMOLEDs to provide richer colours, faster response times, and true blacks, whereas TFT LCDs rely on external backlighting. TFT LCDs are less vivid but more cost-effective for devices that don’t need the same level of colour precision.
Conclusion
TFT LCD technology remains a crucial part of modern electronics due to its balance of affordability, sharp image quality, and versatility. While it faces competition from newer technologies like OLED and AMOLED, its widespread use in smartphones, tablets, monitors, and automotive displays proves its relevance. TFT LCDs offer reliable performance with reasonable power efficiency and have evolved to meet the demands of various industries. Despite its limitations, TFT LCD continues to impact the display industry with its cost-effective solutions and consistent improvements.