Apple’s iPhone operating system reached a major milestone with iOS 4, which included features like app folders and multitasking. It was released on June 21, 2010. This update enhanced the user experience with improved mail capabilities and customization options. iOS 4 showcased Apple’s commitment to innovation, setting the stage for future advancements. Its release was pivotal in the history of iOS development.
Key Features of iOS 4
Multitasking
The introduction of multitasking for third-party apps in iOS 4 revolutionized the user experience, allowing apps to run in the background. This meant users could switch between apps seamlessly, without any interruption. This significantly improved app functionality, enabling features like background audio playback, VoIP calls, and location services, all while maintaining the smoothness of the user experience.
Folders for Apps
iOS 4 introduced the ability to organize apps into folders, greatly enhancing home screen organization. This feature allowed users to group similar apps, reducing clutter and making it easier to find and access their favorite applications. The improved home screen organization provided a more streamlined and efficient user experience.
Improvements and Enhancements
Unified Inbox
iOS 4 introduced a unified inbox, consolidating multiple email accounts into a single, easy-to-manage inbox. This enhancement improved email management by allowing users to view all their emails in one place, streamlining the process of checking and responding to messages across different accounts.
iBooks
The launch of iBooks brought a new dimension to the iOS ecosystem, offering users a dedicated app for reading and purchasing e-books. With features like customizable fonts, search functionality, and interactive elements, iBooks significantly enhanced the e-book reading experience, making it more accessible and enjoyable.
Performance and Interface
Speed and Performance Enhancements
iOS 4 significantly improved overall system performance, making the OS more efficient and responsive. Users experienced faster app launches, smoother transitions, and a general boost in the speed of daily operations, contributing to a more seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Visual and Interface Changes
This update also introduced several visual and interface changes, including updates to the user interface and changes in app icons and layout. These refinements provided a fresh, modern look to the OS, making it more visually appealing and user-friendly while maintaining Apple‘s intuitive design.
Integration and Connectivity
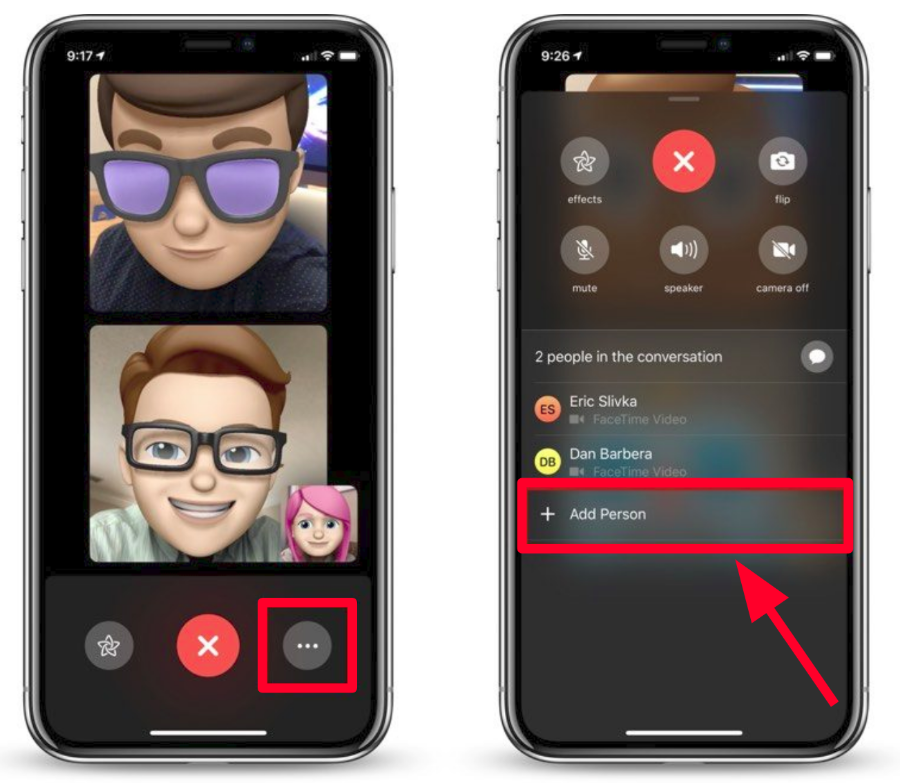
FaceTime
iOS 4 introduced FaceTime, Apple’s video calling feature, which revolutionized communication by allowing users to make video calls with ease. This feature significantly impacted social interaction, making it more personal and engaging by enabling face-to-face conversations regardless of distance.
AirPrint and AirPlay
The introduction of AirPrint in iOS 4 enabled wireless printing, allowing users to print documents directly from their iOS devices without additional drivers or software. Similarly, AirPlay facilitated streaming media from iOS devices to compatible speakers and displays, enhancing the convenience and connectivity of the Apple ecosystem by enabling seamless media sharing and playback.
New Apps and Updates
Game Center
The introduction of Game Center in iOS 4 created a social gaming network where users could connect with friends, track achievements, and compete on leaderboards. This feature enhanced the gaming experience by fostering community and competition among players.
iAd Platform
Apple also introduced the iAd platform with iOS 4, providing developers with a way to monetize their apps through in-app advertisements. This platform offered rich media ads that integrated seamlessly into the app experience, benefiting developers and advertisers by creating a new revenue stream while maintaining user engagement.
Device Compatibility
Supported Devices
iOS 4 was compatible with several Apple devices, including the iPhone 3G, iPhone 3GS, iPhone 4, iPod Touch (2nd generation and later), and the first-generation iPad. This broad compatibility ensured that a wide range of users could benefit from the new features and improvements introduced with this update.
Notes on Performance Differences Across Devices
While iOS 4 brought significant enhancements, the performance varied across different devices. Newer models like the iPhone 4 and iPhone 3GS enjoyed smoother and faster performance due to their more advanced hardware. In contrast, older devices like the iPhone 3G experienced some limitations, with slower responsiveness and reduced feature availability, highlighting the importance of hardware advancements in maximizing the benefits of software updates.
Security and Privacy
Enhanced Security Features
iOS 4 introduced several improvements in security measures, reinforcing the protection of user data and device integrity. Enhanced encryption, better app sandboxing, and more robust protection against malware were key security enhancements that provided users with greater peace of mind.
New Privacy Controls and Settings
Alongside security improvements, iOS 4 also introduced new privacy controls and settings. These included more granular control over app permissions, allowing users to manage what data apps could access, and new location service settings that offered users greater transparency and control over how their location data was used and shared.
Challenges Faced by iOS 4
- Performance Issues on Older Devices:
- iPhone 3G struggled to handle new features smoothly
- Slower responsiveness and reduced feature availability
- Battery Drain:
- Multitasking and resource-intensive features led to faster battery consumption
- Compatibility Limitations:
- Certain apps were not compatible with older models initially
- Key features lacked support on some older devices
- User Dissatisfaction:
- Users of older devices experienced significant performance degradation
- Balancing new features with backward compatibility was challenging
Legacy and Impact
Market Reception and User Feedback:
- iOS 4 received positive reviews for its innovative features like multitasking and app folders.
- Users appreciated the improved customization and organizational capabilities despite some performance issues on older devices.
- The introduction of FaceTime and Game Center was particularly well-received, enhancing social interaction and gaming experiences.
Long-term Impact on Future iOS Versions
- iOS 4 set a precedent for subsequent iOS updates, influencing the development of new features and improvements.
- The multitasking framework and enhanced security measures became foundational elements for future versions.
- The success of iBooks and the iAd platform demonstrated the potential for new app categories and monetization strategies.
Comparison with Previous iOS Versions
Key Differences Between iOS 4 and Its Predecessors:
- iOS 4 introduced multitasking for third-party apps, a significant upgrade from the single-tasking nature of earlier versions.
- The addition of app folders allowed for better home screen organization, unlike the more cluttered layout of previous versions.
- Enhanced mail management with the unified inbox was a major improvement over the simpler email handling in earlier iOS iterations.
Evolution of Features and Functionalities:
- iOS 4’s multitasking and app folder features paved the way for more sophisticated task management and app organization in later versions.
- Security enhancements and privacy controls introduced in iOS 4 laid the groundwork for more robust security features in future updates.
- Innovations like FaceTime and Game Center evolved and expanded, becoming integral to the iOS ecosystem.
Conclusion
iOS 4 was a pivotal release in Apple’s mobile operating system history, introducing major features such as multitasking, app folders, and the unified inbox, significantly enhancing user experience and system functionality. The launch of FaceTime and Game Center and improved security and privacy measures showcased Apple’s commitment to innovation. Despite some challenges, iOS 4 set the stage for future developments, solidifying its place as a transformative update that influenced the evolution of subsequent iOS versions.